Therefore, By Giving Back The Stem Cells That Are Much Needed Would Have Tremendous Health Benefits.
WHERE DO WE GET THE STEM CELLS
COMPARISON OF STEM CELLS
WE OBTAIN STEM CELLS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD, ADIPOSE TISSUE AND BONE MARROW
| TYPE | ORIGIN | EXTRACTION METHOD | RISK ANALYSIS |
| Embryonic Stem Cell (hESC) | Inner Cell Mass (ICM) of Embryo (Allogenic) |
Cultivate the inner cell mass in the fertilized egg |
|
| induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPS) | Induced from Epidermic Cell (Autologous) |
Made from genetically introduced into adult cells |
|
| Dental Pulp Stem Cells (hDPSCs) | Deciduous teeth, gums, periodontal ligaments, wisdom teeth (Autologous) |
Natural loss (deciduous teeth) or mannually obtained (gum, periodontal ligament, wisdom tooth) |
|
| Bone Marrow Stem Cell (BMSC) | Bone Marrow (Autologous/ Allogenic) |
Bone marrow aspiration |
|
| Adipose Stem Cell (ADSC) | Fat (Autologous) |
Liposuction (surgical) procedures |
|
| Peripheral Blood Stem Cell (PBSC) | Peripheral blood (Autologous) | Apheresis procedures |
|


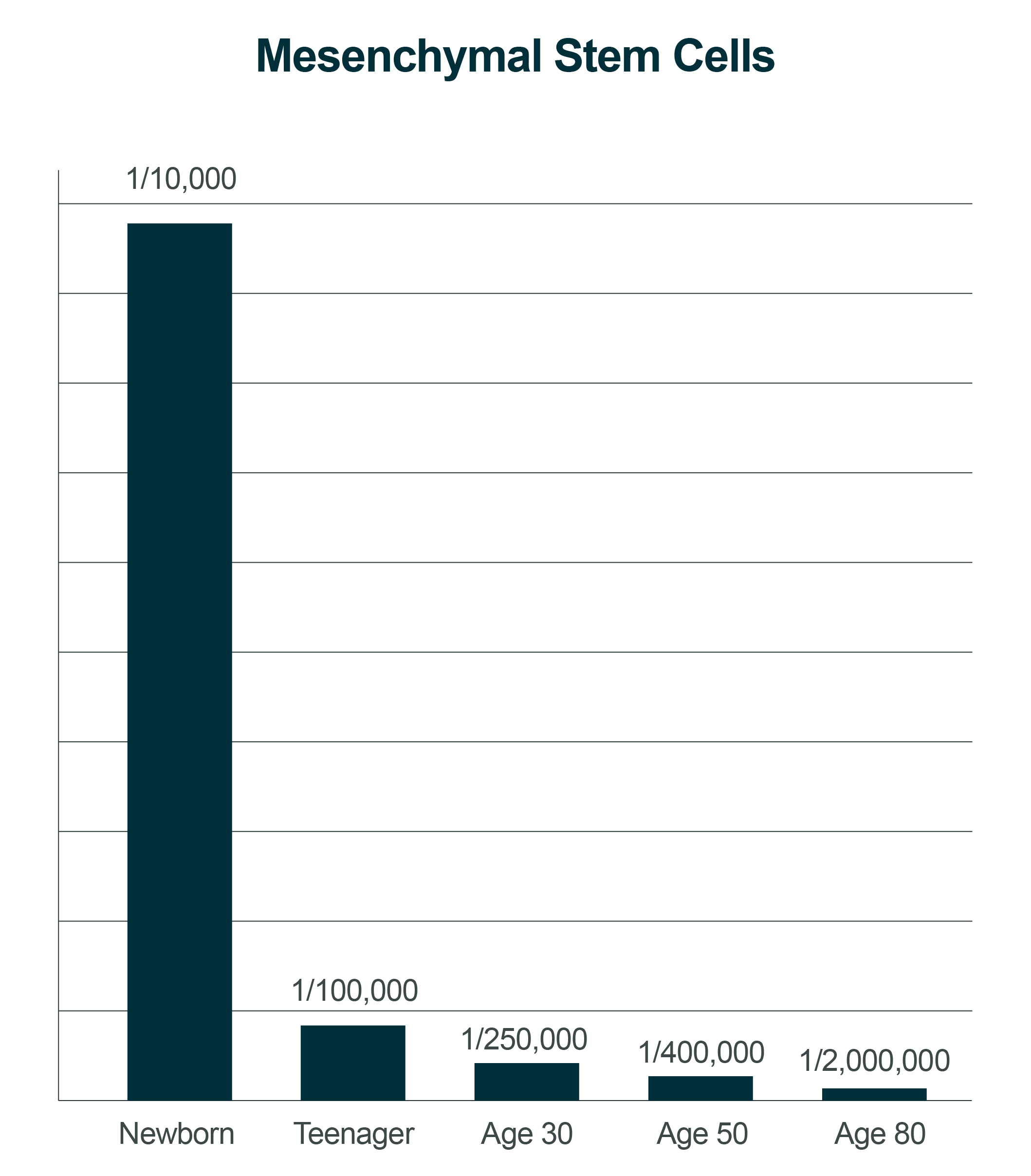 Studies have shown that in a population of Alzheimer’s disease and coronary artery disease patients there is a significant reduction in the number of endothelial precursor cells (a type of stem cell) in the body. Endothelial precursors cells are believed to be responsible for blood vessel formation. With the reduction of endothelial precursor cells causing a reduction of vascularity in the body would also contribute to erectile dysfunction in male or hypertension.
Studies have shown that in a population of Alzheimer’s disease and coronary artery disease patients there is a significant reduction in the number of endothelial precursor cells (a type of stem cell) in the body. Endothelial precursors cells are believed to be responsible for blood vessel formation. With the reduction of endothelial precursor cells causing a reduction of vascularity in the body would also contribute to erectile dysfunction in male or hypertension.